Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Igawa, Naoki; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Shimura, Kenichiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 242(1-2), p.469 - 472, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.19(Instruments & Instrumentation)SiC/SiC composites are one of the candidate materials for first wall in a fusion reactor because of their high strength at high temperature and low residual radioactivity after irradiation. In the fusion reactor, these materials are required to have high thermal diffusivity for heat exchange and reducing the thermal shock. Under fusion conditions, helium (He) and hydrogen (H) are produced in SiC. In this study, the effect of He ions implantation on the thermal diffusivities of SiC and SiC/SiC composite were investigated. In the results, the thermal diffusivities of SiC and SiC/SiC composites decreased after He ions implantation. However, the thermal diffusivities of SiC and SiC/SiC composites hardly reduced in the operation temperature of fusion reactor. The thermal diffusivities of He implanted specimens were partly recovered by annealing. The defect concentration induced by He implantation, X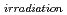 , in SiC/SiC composites was estimated. The X
, in SiC/SiC composites was estimated. The X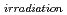 rapidly decreased around 500
rapidly decreased around 500  C. The reason is that the He release from SiC starts at 500
C. The reason is that the He release from SiC starts at 500  C.
C.
Takeyama, Akinori; Yamamoto, Shunya; Ito, Hiroshi; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 232(1-4), p.333 - 337, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)Cu precipitates were formed on Si(100) by 200 keV Cu ion implantation and subsequent annealing at 773 K. The shape of the Cu precipitates evolved from a large rectangle to a small elongated pyramid with increasing annealing time. This shape evolution seemed to result from the epitaxial formation of Cu precipitates to minimize the interfacial energy between the precipitate and the Cu implanted substrate. The average density of Cu precipitates monotonously increased and the average diameter of Cu precipitates decreased with increasing annealing time up to 1 h. These indicate that the morphology, size and average density of Cu precipitates can be controlled by varying annealing time, and that Cu ion implantation and subsequent annealing were effective in producing a substrate dispersed with catalytic particles for oxide nanorods growth.
Takeyama, Akinori; Yamamoto, Shunya; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Ito, Hiroshi
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 44(1B), p.750 - 753, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)Pyramid shaped Cu precipitates were formed on Si (100) surface as a result of 200 keV Cu ion implantation and subsequent annealing. Then, ZnO nanorods were successfully synthesized on the Cu implanted substrates by chemical vapor transport (CVT). Hexagonal shaped nanorods with a diameter of 200 nm were grown nearly perpendicular to the Cu implanted substrate and their average density was increased as increasing that of Cu precipitates. The facts strongly indicate the Cu precipitates served as the catalytic particles for the growth of ZnO rods.
 ions
ionsLee, C. G.; Omura, Takahito*; Takeda, Yoshihiko*; Matsuoka, Saburo*; Kishimoto, Naoki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 326(2-3), p.211 - 216, 2004/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Magnesium aluminate spinel of single crystal was irradiated with 60 keV Cu at a dose rate up to 100
at a dose rate up to 100  A/cm
A/cm , to a total dose of 3
, to a total dose of 3 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm , in order to study changes in hardness and step-height swelling by high-flux implantation. Hardness determined by nano-indentation measurements steeply decreased with implantation. There is a strong negative correlation between dose-rate dependences of the hardness and the step-height swelling: the former decreases as the latter increases. The Rutherford Backscattering Spectrometry (RBS)/channeling measurements showed that the spinel is not completely amorphized over the dose-rate range in this study, and the radiation-induced softening observed is not due to amorphization. Results of optical absorbance suggested that radiation-induced point defects and their clusters on the anion sublattices of the spinel played an important role in the radiation-induced swelling under high-flux ion implantation.
, in order to study changes in hardness and step-height swelling by high-flux implantation. Hardness determined by nano-indentation measurements steeply decreased with implantation. There is a strong negative correlation between dose-rate dependences of the hardness and the step-height swelling: the former decreases as the latter increases. The Rutherford Backscattering Spectrometry (RBS)/channeling measurements showed that the spinel is not completely amorphized over the dose-rate range in this study, and the radiation-induced softening observed is not due to amorphization. Results of optical absorbance suggested that radiation-induced point defects and their clusters on the anion sublattices of the spinel played an important role in the radiation-induced swelling under high-flux ion implantation.
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Nishi, Masataka; Sugisaki, Masayasu*
JAERI-Research 2003-018, 32 Pages, 2003/09
Tritium transport behavior in materials, which is essential for the safety evaluation of the fusion reactor, has to be evaluated by either tritium properties or extrapolated value from protium or deuterium (D) to tritium (T) using the isotope effect theory. However, there are still some uncertainties on estimation of T behavior in materials, because there are only a few T transport properties data in materials, and it is not completely proven the application of the isotope effect theory to T due to the lack of T data. Therefore, in order to understand the tritium transport properties in materials, isotope effects on diffusion and surface recombination between T and D in/on nickel, whose hydrogen transport properties were well known, were investigated by comparing the obtained properties of T with those of D measured under the same conditions with the ion driven permeation method. Though obtained diffusion coefficient of T was larger than that of D, and activation energy of diffusion of T was smaller than that of D as the contrary to the classical diffusion theory, those were shown to be explained with a modified diffusion theory by introducing higher vibration temperatures in nickel than previous reported values. In addition, the isotope effect on surface recombination coefficient between D and T was shown to be explained using a modified solution model as well as diffusion.
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Nishi, Masataka; Morita, Kenji*
JAERI-Research 2003-016, 32 Pages, 2003/08
As a part of the detritiation study from the fusion reactor materials, chemical state of tritium injected into Sr-Ce base oxide ceramic proton conductor, which is a candidate for a tritium recovery system, was investigated with thermal desorption method. The results indicated that the oxide has to be heated up over 1300K to remove tritium due to the OT bond formation in the oxide. On the other hand, tritium removal behavior from the oxide were also investigated by exposing to humid air, and the mechanism of tritium removal from the oxide was identified by the dependency of tritium removal amount and chemical state on the humidity. The results revealed that tritium removal rate by the air exposure was low, and that almost tritium was removed as the vapor form, which was attributed to the isotope exchange reaction between the OT bond on the surface and the protium in vapor. It was also found that small amount of tritium was removed as elemental form under the humid air exposure, which could be attributed to the solute tritium in the oxide and oxygen absorption to the oxygen deficit in the oxide. As a result, the difference of the detritiation mechanism exposed to the humid air on the chemical state of tritium in the oxide was clarified, and it could be a useful basic data for the optimization of detritiation method.
Wei, P.; Xu, Y.; Nagata, Shinji*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Naramoto, Hiroshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206(1-4), p.233 - 236, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:43.07(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Tsuji, Hirokazu; Tsukada, Takashi
Proceedings of 11th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-11) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2003/04
Irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) of austenitic stainless steel has been studied as main concern of an aging problem of light water reactor (LWR) materials. It is essential to evaluate corrosion behavior of irradiated materials for mechanistic understanding of IASCC. The aim of this work is to evaluate the corrosion behavior of ion irradiated materials using atomic force microscope (AFM), and evaluate the influence of radiation temperature, radiation damage, H and He implantation.
Morita, Kenji*; Suzuki, Hironori*; Soda, Kazuo*; Iwahara, Hiroiku*; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Nishi, Masataka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 307-311(2), p.1461 - 1465, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.03(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Nishi, Masataka; Arita, Makoto; Okuno, Kenji*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 55(4), p.513 - 520, 2001/09
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:56.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Abe, Hiroaki
Diamond and Related Materials, 10(3-7), p.1201 - 1204, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:63.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Abe, Hiroshi; Uedono, Akira*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Komatsu, A.*; Okada, Sohei; Ito, Hisayoshi
Materials Science Forum, 363-365, p.156 - 158, 2001/05
no abstracts in English
 F
F compounds in fluorine-implanted TiO
compounds in fluorine-implanted TiO
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Sumita, Taishi; Yamamoto, Shunya
Journal of Materials Science Letters, 21(1), p.33 - 35, 2001/01
Times Cited Count:89 Percentile:91.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We showed the effects of 200 keV F implantation in TiO
implantation in TiO rutile single crystals followed by the thermal annealing. The isochronal annealing at 573 and 873 K for 5 h for each step led to the formation of an F-doped TiO
rutile single crystals followed by the thermal annealing. The isochronal annealing at 573 and 873 K for 5 h for each step led to the formation of an F-doped TiO phase, along with the recovery of the radiation damage and the simultaneous impurity diffusion. This phase was identified to be a TiO
phase, along with the recovery of the radiation damage and the simultaneous impurity diffusion. This phase was identified to be a TiO F
F compound with x = 0.0039 in the outmost region as determined by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (probably the first few atomic layers). The fluorination of TiO
compound with x = 0.0039 in the outmost region as determined by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (probably the first few atomic layers). The fluorination of TiO leads to interesting characteristics and opens avenues towards photoelectronic films with various applications. In addition, our method enabled dopants to be introduced in a controlled manner at specific locations to realize impurity concentration gradients in TiO
leads to interesting characteristics and opens avenues towards photoelectronic films with various applications. In addition, our method enabled dopants to be introduced in a controlled manner at specific locations to realize impurity concentration gradients in TiO .
.
Abe, Hiroaki
Hoshasen To Sangyo, (88), p.54 - 60, 2000/12
no abstracts in English

 -ion implanted SUS304 stainless steel by in situ SR-XPS, 2; Chemical state of oxygen
-ion implanted SUS304 stainless steel by in situ SR-XPS, 2; Chemical state of oxygenLi, Y.; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro
Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 20(6), p.331 - 337, 2000/12
no abstracts in English
Abe, Hiroaki; Yamamoto, Shunya; Miyashita, Atsumi
Dai-11-Kai Ryushisen No Sentanteki Oyo Gijutsu Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu (BEAMS 2000) Hobunshu, p.127 - 130, 2000/11
no abstracts in English
Naramoto, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Narumi, Kazumasa
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 161-163, p.534 - 538, 2000/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:20.05(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Goto, Masahiro*; Kawanishi, Shunichi; Fukumura, H.*
Applied Surface Science, 154-155, p.701 - 705, 2000/02
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:61.51(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 produced by low-energy ion implantation
produced by low-energy ion implantationAli, M.; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Li, Y.; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki
Photon Factory Activity Report 1998, P. 36, 1999/11
no abstracts in English
Naramoto, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Narumi, Kazumasa
JAERI-Review 99-025, TIARA Annual Report 1998, p.191 - 192, 1999/10
no abstracts in English